Gratuity rules are applicable to those working in an organisation, whether in a private or government. The rules of Gratuity were first introduced in 1972 with the launch of the Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972.
Gratuity is a token of appreciation for an employee’s continuous service in a company for at least five years. It is a one-time payment, and hence, the worker can obtain it either after his/her retirement or after serving for a minimum of five years in the same company.
Earlier, the payment of Gratuity was limited to ₹ 10 lakh. In case the Gratuity amount would go beyond that, the employee was liable to pay the required tax on that amount. However, with the introduction of the Gratuity new rules of 2020, the threshold for tax on the Gratuity amount has been increased to ₹ 20 lakh.
Amazing, right? Keep reading, and it will get even more interesting and insightful.
An Overview of Gratuity
Gratuity is the amount of money that employees receive from their organisation for continuously serving in the same company for at least five years. Technically, it is a token of appreciation for employees as a favour for providing their consistent service to the company.
The Gratuity is regulated and governed by the Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972. According to the provisions of this Act, an employee is entitled to get the Gratuity money before five years of service only if he/she gets disabled in an accident or due to a disease.
The Gratuity amount entirely depends on the terms of service you have offered to the company and the last drawn salary.
Keep reading further to know how to calculate Gratuity for employees in different conditions.
Gratuity Rules: According to Gratuity Act, 1972
According to the Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972, the following are the rules of Gratuity:
1. Gratuity is Payable for Companies with Ten or More Employees
Any organisation that has a workforce of ten or more employees in the preceding twelve months is accountable to pay Gratuity. Even if the number of employees in the company goes below ten, it will still be liable to pay the Gratuity, as the Act says.
2. Employees Must Complete 5 Years of Service to Be Qualified for Gratuity
Any person seeking Gratuity from a company should have rendered at least five years of continuous service to the organisation. Nevertheless, the condition doesn’t apply in cases of demise or if the employee becomes disabled.
The calculation of Gratuity differs depending on the kind of employment. For instance, to calculate the amount of Gratuity for the five years, a single year is estimated as 240 working days in the company for employees who don’t work underground.
However, for the people working underground, such as in mines and other areas, a year is considered to be 190 days.
Let us now consider another case.
Let’s hypothetically assume Mira has worked for 4 years and 8 months in a company. It will be considered as 5 years. On the contrary, if she has worked for 4 years and 2 months, it will be counted as 4 years only. This means that she will be entitled to receive a Gratuity only in the first case.
The continuous service of five years also comprises interruptions caused by the lockout, strike, layoff, absence from duty without leaves, accident, and termination of service not on the employees’ part.
3. Gratuity can be Availed in Various Other Cases than Just upon Retirement
According to the Gratuity rules, employees will be entitled to receive the Gratuity amount upon:
- Resignation
- Retirement
- Disablement due to a Disease or Accident
- VRS
- Termination
- Lay Off because of Retrenchment
4. The Calculation of Gratuity Depends on the Last Drawn Salary and Years of Service
The calculation of Gratuity depends on the employee’s last drawn salary plus the years of service. However, the formula for calculation varies from the applicability of the Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972.
- Calculating Gratuity – For Employees Covered under the Act
As stated earlier, a company with ten employees is covered under this Act.
The Gratuity calculation in such companies could be done using the formula described below:
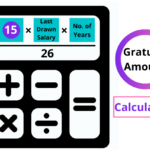
Gratuity = 15 X b X n / 26
Where b= Last drawn salary = Last drawn basic salary + dearness allowance, and
n = Years of service in the organisation.
For example, Soniya worked with XYZ company for 8 years. Her last drawn basic salary plus the dearness allowance (DA) was ₹ 60,000.
Therefore, the Gratuity amount = 15 x 60,000 x 8 / 26 = ₹ 2,76,923.
Here,
- The last drawn salary comprises basic and dearness allowance (DA). Any other element of income won’t be included in the salary.
- Calculating Gratuity – For Employees Not Covered under the Act
For employees who aren’t covered under this Act, the Gratuity calculation for them can be done using the following formula:
Gratuity = 15 x the working tenure x your last drawn salary / 30.
For instance, Shreya earns a basic salary of ₹ 80,000. She served continuously for 8 years 8 months in the company but doesn’t fall under the Gratuity Act. Therefore, her tenure will be considered eight years only. Hence,
The Gratuity Payment = 15 x 80,000 x 8 / 30 = ₹ 3,20,000.
Here,
- The salary consists of the basic salary, dearness allowance, and commissions. Any other component of salary won’t be included.
- The number of years employed is only considered based on the completion of each year of service.
5. Gratuity can be Terminated for Various Reasons
According to the rules of Gratuity, employers can refuse to pay an employee’s Gratuity which has been terminated for the following reasons:
- Involvement in an offence concerning moral turpitude
- Disorderly conduct or riotous conduct or any other violent Act
6. Employers can’t Forfeit the Gratuity Money Even during Bankruptcy
Even if the employer goes bankrupt, they are still accountable to pay Gratuity to its workers. No order or court decree can restrict an employer against it.
7. Gratuity Amount of up to ₹ 20 Lakh is Exempted from Taxation
As per Gratuity Rules, 2021, a Gratuity amount of up to ₹ 20 lakh is paid by companies covered under the Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972. Previously, this threshold was fixed to ₹ 10 lakh.
8. Income Tax on Gratuity Differs for Different Employees
| Type of Organisation | Gratuity Tax Implications |
|
Covered under the Gratuity Act |
Doesn’t apply to the following:
|
|
Not Covered under the Gratuity Act |
Doesn’t apply to the following:
|
|
Central/State Government, Local Government Authorities, and Defence |
Not applicable |
9. ₹ 20 Lakh Limit for Tax Exemption is for Cumulative Gratuity Obtained
The tax exemption for the limit of ₹ 20 lakh is for cumulative Gratuity money obtained. For instance, Mira worked continuously with a company for 20 years and got a Gratuity of ₹ 19 lakh.
She joined another organisation, and after eight years of service, she received a Gratuity of another ₹ 7 lakhs. In total, she got a Gratuity of ₹ 26 lakhs. Therefore, as per the Act, she will have to pay a tax of ₹ 6 lakh (₹ 26 Lakh – ₹ 20 Lakh) to the government.
10. Gratuity Paid to the Legal Heir or Widow of the Employee should be Exempted of Tax
If an employee dies, the Gratuity amount that his legal heir or widow receives will be exempted from tax. Moreover, any ex-gratia payment in the name of an employee or his legal heir due to any injury caused will also be tax-free.
Provisions of Gratuity Rules 2020
For employees who are working on contracts or on a fixed-term basis, the new rules have been made specifically for them. Every employee who works for an organisation on a contract or for a fixed term of one year, that person is entitled to receive Gratuity.
The contract employee will now be provided with social security rights like a regular employee. Besides the contract employees, those working in the seasonal firms can also render the benefits.
To clarify, only a few rules have been altered, otherwise, the old rule will stay the same. Currently, the calculation of Gratuity is done based on the employees’ salary of 15 days every year on the completion of five years of service. Its maximum limit is set to ₹ 20 lakh, above which the employee would have to pay the tax.
The new Gratuity rules have been mainly altered for those working for a specific period. Such employees are known as contract workers. Let’s find out what the rule says-
Benefits for Contract Workers
The new Gratuity rules are surely in favour of contract or fixed-term employees. As per the provisions of the new rule, there won’t be any condition for a minimum service term. For the first time, a contract worker who is employed for a specified period will be provided with the right to social security just like a regular employee.
When will You Receive the Gratuity Amount?
According to Chapter 5 of the Act, the employee will get a Gratuity for rendering five consecutive years of service in the same organisation at the end of his/her tenure. It could be either on retirement, resignation, disability, or death of an employee from illness or accident.
However, the term of service differs in the case of a working journalist. It will be three instead of five years. Moreover, if the employee dies or becomes disabled, five continuous years of service won’t be required. Also, if somebody is working on a fixed-term basis or any such notice as specified by the Central Government, they are not obligated to complete five years of service.
Gratuity Rules 2021
New Labour Law was implemented from April 1, 2021, under the Four Labour Code. According to the new definition, pension, bonus, PF contributions, HRA, overtime, Gratuity, and conveyance allowance must be eliminated from salary. This implies that the share of the basic salary should be kept at fifty percent or more.
After the introduction of the new Labour Law, it is believed that a big alteration in salary structure is possible. This also means that the in-hand salary of employees could be reduced. On the contrary, the deduction in favour of social security schemes such as the PF (Provident Fund) will increase.
The new rule also states that allowances of an employee must not exceed 50 percent of the total salary. As a result, employers would be bound to increase the basic salary of their employees by fifty percent. The new rule is initiated to render more benefits on retirement than before.
Also, the Department of Pension and Pensioners’ Welfare (DoPPW) released “Pension Rules 2021,” which states that a Government servant who has completed five years of service and is qualified for pension or service Gratuity under Rule 44 will receive retirement Gratuity equal to one-fourth of emoluments for every six-monthly period of the qualifying term.
Death Gratuity
If the qualifying service term is less than one year, the Gratuity to be paid is twice the emoluments.
If the qualifying service term is one year or more but less than five years, the Gratuity payable is six times the emoluments.
In case the qualifying service term is five years or more but less than eleven years, the Gratuity payable is twelve times the emoluments.
If the qualifying service term is eleven years or more but less than twelve years, the Gratuity payable is twenty times the emoluments.
In case the qualifying service term is twenty years or more, the Gratuity payable is half of the emolument for every six-month period of the qualifying term completed. Also, it is subject to a maximum of 33 times or emoluments.
The aforementioned death Gratuity also applies if any government servant dies in a suicide.
| NOTE
In case a government retired servant passes within five years from the date of retirement and without obtaining an amount of Gratuity, then the family of a deceased will receive a residuary Gratuity as per the Pension Rules of 2021. |
Qualifying Service
To compute the length of qualifying service or term, a part of a year equivalent to three months and above will be considered as a completed six month time. Moreover, it will be regarded as a qualifying service.
If an employee has served for 4 years and 7 months or more but not five years to be exact, then his/her qualifying service for calculating the Gratuity will still be considered as five years. Also, they will be totally qualified for retirement Gratuity.
Dearness Allowance
As per the Pension Rules 2021, DA (Dearness Allowance) admissible on the date when the employee retires or dies must also be treated as emoluments for the purpose of calculating the Gratuity.
Frequently Asked Questions About Gratuity Rules:
Q1. What is the new rule of Gratuity 2021?
Ans: According to the new Gratuity rules 2021, employers must increase the basic salary of their employees by fifty percent. This will, in turn, increase the employer’s payment of employee Gratuity.
Q2. What are the new rules for a contract worker?
Ans: According to the new rules of Gratuity, there won’t be any condition for a minimum service term. For the first time, a contract worker who is employed for a specified period will be provided with the right to social security just like a regular employee.
Q3. Are 3 years eligible for Gratuity?
Ans: Since the minimum eligibility for Gratuity is 5 years, anybody with 3 years of service won’t be eligible for availing of Gratuity until it’s a case of disability caused by accident or due to any disease. Also, if you are a contract employee employed for three years of service, then you might receive Gratuity, as per new rules.
Q4. Are 4 years 7 months eligible for Gratuity?
Ans: The minimum period of service required for obtaining Gratuity is to work at least for 5 years in the same company. However, those covered under the Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972, will consider this period as 5 years, and the employee working under such an organisation will be entitled to receive Gratuity.
Nevertheless, employers not covered under the Act won’t pay the Gratuity to an employee until she/he has completed the exact five years of service in the company.